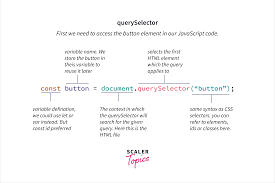
When to Use querySelector
- You want to change or read a specific element's text, style, or content.
- You're adding interactivity (like reacting to button clicks or form input).
- You need to update parts of a page dynamically without reloading.
- You want to select elements using flexible CSS-style rules.